Discussion #6:
Michelangelo's The Last Judgment
Smart History: Michelangelo, Last Judgment, Sistine Chapel, fresco, 1534-1541
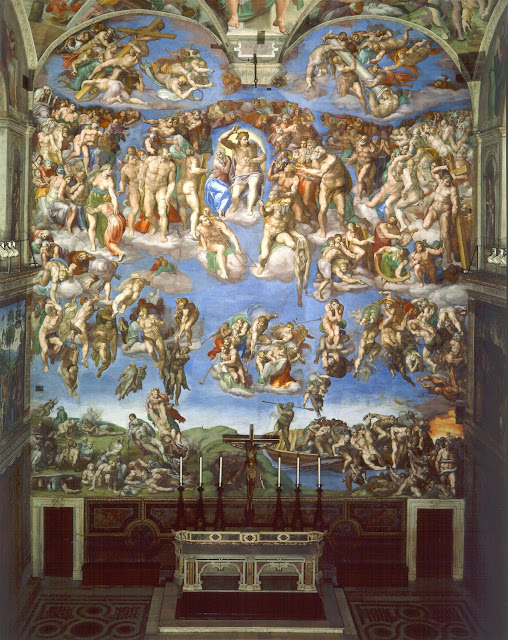 |
| Michelangelo, The Last Judgment, Fresco in the Sistine Chapel 1537-1541 |
|
|
Michelangelo's The Last
Judgment is a fresco on the
altar wall of the Sistine Chapel in the Vatican. It was unveiled in
October of 1541, Michelangelo completed the painting in five years
time (Hall, 132). The numerous nudes inside of the chapel was very
controversial. It was even during Michelangelo's lifetime that some
argued the fresco should be torn down, or manipulated, “Pope Paul
seriously considered having the fresco destroyed” (Hall, 189). The
Pope even asked Michelangelo “to fix the nudes himself; the painter
replied, “Tell the pope that it is a small matter, but let him fix
the world, pictures are quickly mended” (Hall, 189). The decision
to correct some of Michelangelo's errors was ordered before his death
in February of 1564 (Hall, 190). It was throughout the seventeenth
and eighteenth centuries that loincloths and drapery were added to
the figures, some of these cover-ups were removed in the latest
restoration (Hall, 190). However not all of these additions were
removed because “they had become a historical part of the painting”
(Hall, 190).
These images in The Last
Judgment have been argued to
violate the second commandment “You shall not make for yourself any
graven image” (Hall, 190). The nudity was opposed because it was
“feared that it would distract and make the image ridiculous”
(Hall, 192).
Although this grand fresco ruffled
a lot of people's feathers, it was one of the most widely copied and
distributed paintings in Europe (Hall, 192). Because of the
inexpensive medium of printmaking, a wider audience could now view
the artwork. An uneducated audience laughed at the fresco rather than
“being moved to devotion” (Hall, 192). It is thought that because
of this change in audience (The Last Judgment was
only meant for those with access to the Papal chapels) that
encouraged the Church to “correct” the painting (Hall, 192).
Marcia Hall's excerpt on
Michelangelo's The Last Judgment
was more factual based without much emotion behind the
interpretations of the fresco. Leo Steinberg's “Michelangelo's Last
Judgment as Merciful Heresy” had much more attitude and passion.
Steinberg suggests that Michelangelo doubted the eternal torment of
sinners and the vindictive, retributive nature of the Last Judgment –
which was committing heresy in the the 1500's (3). Michelangelo's
Last Judgment scene is radically different from previous and
contemporary depictions in that: Christ is not seated as a judge,
Christ is not angry, there are no distinctions of the angels, and no
distinct separation of Heaven and Hell. Steinberg interprets the
ambiguity of the composition and the emotions of the figures to be
purposeful, to be based on what Michelangelo really thought of his
religion in his later years. Here I have comprised a list of his
arguments that back up his theory:
- The intent in Michelangelo's Christ is unknowable
- That the imperturbability of Christ's face turns all interpretation into projection
- That the gesture of Christ reveals a mystery, not a foregone conclusion
- That the Virgin is not represented as scared
- That the robust corporeality of the Saved expresses the meaning of Resurrection
- That the artist's self-portrait as empty skin signals his anxiety to partake in the Resurrection
- That there is no gap between Heaven and Hell
- That Michelangelo disbelieves in material Hell
- That the tumblers above are no sinners but allegories of Sin
- That Michelangelo's apocalyptic demography is unorthodox
- That the unequal sizes of the books do not express a statistical differential
- That the punishment in Michelangelo's fresco is not to be everlasting
- Theological excursus showing that Michelangelo's fresco embodies a merciful heresy
- That the Martyrs' supposed clamor for vengeance, being inaudible may not have been heard aright
- That the interpretative tradition feeds on itself, with minimal interference form the object interpreted
I
find all of Steinberg's research and arguments to be convincing.
Although I cannot help but remember previous readings like “Artistic
Theory in the High Renaissance” where Sir Anthony Blunt explains
Michelangelo's change of faith later in life. This metamorphosis in
Michelangelo's thinking was documented in his writing/poetry and in
his later work. The body was no longer so important to Michelangelo,
the spirit was his concern and he became very introspective.
Michelangelo worried about his soul's resurrection; whether he had
lead a Christ-like life that would be worthy of Heaven.
It
is with that previous article, and Steinberg's, that I wonder if
Michelangelo's The
Last Judgment
was a sort of art therapy for the artist? Was it his way of working
through the turmoil he felt throughout his long life? I'd like to
believe that Michelangelo was intentional in every decision he made
in this Fresco, that every lengthy interpretation by Steinberg was
exactly what he was thinking and trying to say. Michelangelo was an
apt thinker and gifted artist – a genius – but I doubt he would
be brave enough to depict a scene worthy of heresy directly in front
of the Papacy. He went into hiding once before because he feared
murder, I don't believe he would ever have put himself in harms way.
But
perhaps Michelangelo knew that his Last
Judgment
would go directly over the church's head. ...As you can tell this
argument makes me waffle in between agreeing and disagreeing. Maybe
the class discussion will put me on one side or the other.
P.S. For your enjoyment (and mine because I am a Printmaker) I have linked to the prints/engravings mentioned at the end of Leo Steinberg's “Michelangelo's Last
Judgment as Merciful Heresy” which
was on page 14 of the article. Steinberg mentions the alterations found
in these prints, especially the size differences of Heaven and Hell
that the engravers changed from Michelangelo's original fresco.


























